Plant leaves are green in color as they contain green colored pigment called chlorophyll
Leaves are the photosynthetic organs for green plants.
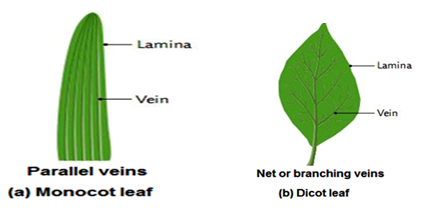 |
| Figure: Monocot and dicot leaves |
External Structure of a Leaf:
The external structure of a leaf consists of the below structures:Petiole:
Petiole is also known as leaf stalk
Petiole is the thin stalk that attaches the leaf to the main stem or branch
Lamina:
Lamina is also known as leaf blade
 |
| Figure: External structure of a leaf |
It is the large broad green surface of the leaf
It gives a large surface for light absorption
Midrib:
Midrib is also known as main vein of the leaf
It is the large central thick vein of the leaf that runs through the leaf blade from its base to its apex.
Leaf margin:
Leaf margin is also known as leaf edges.
Leaf margins are thin which reduce the distance of diffusion of gases between the atmosphere and innermost leaf cells.
Leaf apex:
Leaf apex is also known as leaf tip.
It is the terminal part of the leaf
Veins:
Leaf veins branch from the midrib of the leaf
Leaf veins contain vascular tissue of the leaf (xylem and phloem)
Functions of the Leaf veins |
1)
Provide support for the leaf
2)
Transportation of water and minerals
(through xylem)
3)
Carry away manufactured food from
the leaf plant parts (through phloem)
|
 |
| External structure of a leaf |


No comments:
Post a Comment